SWS3004-Lecture 2: Applications and Paradigms
L2 is about Application and Paradigms of Cloud Computing.
Outline
- Cloud Applications
- Common Features
- Applications
- Challenges in Developing Applications
- Architectural Styles for Cloud Applications
- Cloud Application Development Models
- Characteristics of Cloud Service Models
- Examples of Setting up a Blog
Key Terms
Divisible workload
Performance isolation
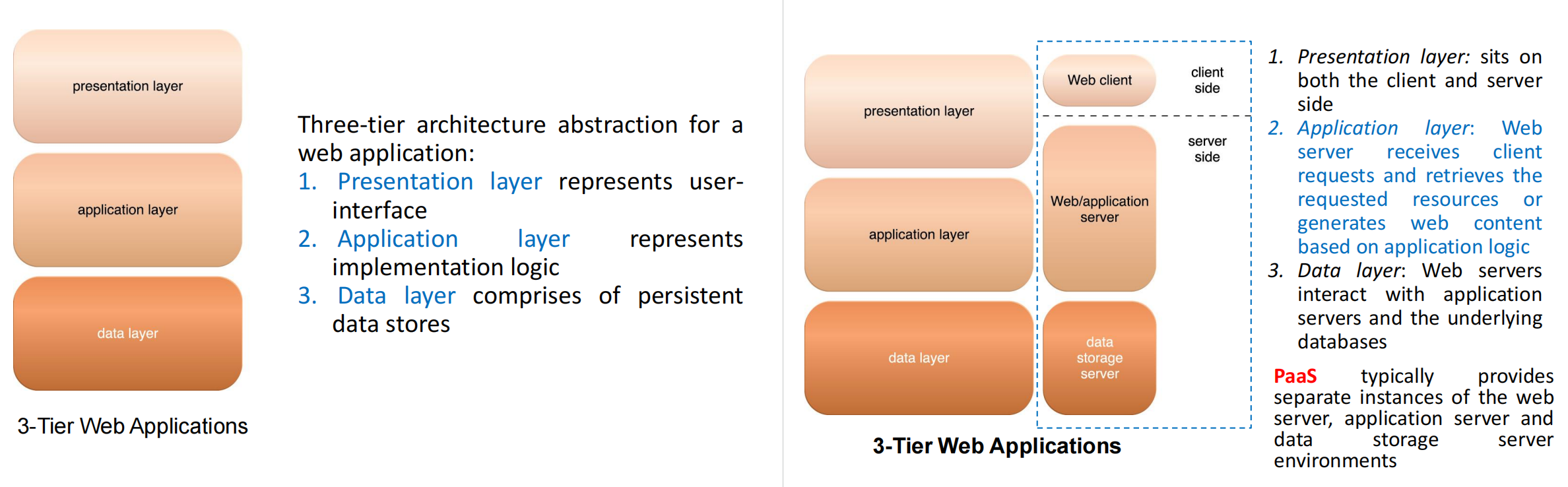
Web application architecture layers
Application development models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
Cloud Applications
Common Features of Cloud Providers
Basic and higher - level services (IaaS -> SaaS).
Compute and storage resources - virtual servers (Linux and Windows) and object store.
Deployment management services - load balancer, auto scaling, message queueing, monitoring, ….
User interface - graphical user interface, command-line interface.
Cloud Applications
- Focus mainly on enterprise computing.
- Ideally, an application can partition its workload into n segments and spawn n instances, and the execution time reduced by a factor close to n. (MapReduce)
- Key Challenges
- cloud consumer: scale application to accommodate a dynamic load, recover after a system failure, efficiently support checkpoint/restart
- cloud provider: manage a large number of systems (cloud consumer applications), provides quality of service guarantee
- Ideal Applications
- web services
- database services
- search services
- machine learning with massive-scale models
- Unlikely to perform well
- applications with a complex workflow and multiple dependencies such as high-performance computing
- applications with intensive communication among concurrent instances
- workload cannot be arbitrarily partitioned
Challenges in Developing Cloud Applications
Performance isolation – how to ensure that customer performance is not affected by other users?
Reliability - major concern, server failures expected when a large number of servers cooperate to compute.
Cloud infrastructure exhibits latency and bandwidth fluctuations which affect the application performance.
Performance considerations limit the amount of data logging (identify unexpected results, errors, monitor application performance).
Architectural Styles for Cloud Applications
Reliance on Internet and web technology (high accessibility, web browser universality, ease of web-based service development).
Cloud services use web technology as both the implementation medium and management interface.
2 basic components of the web are web browser client and web server, i.e., based on client-server architecture.
“as-a-Service” Cloud Delivery Models
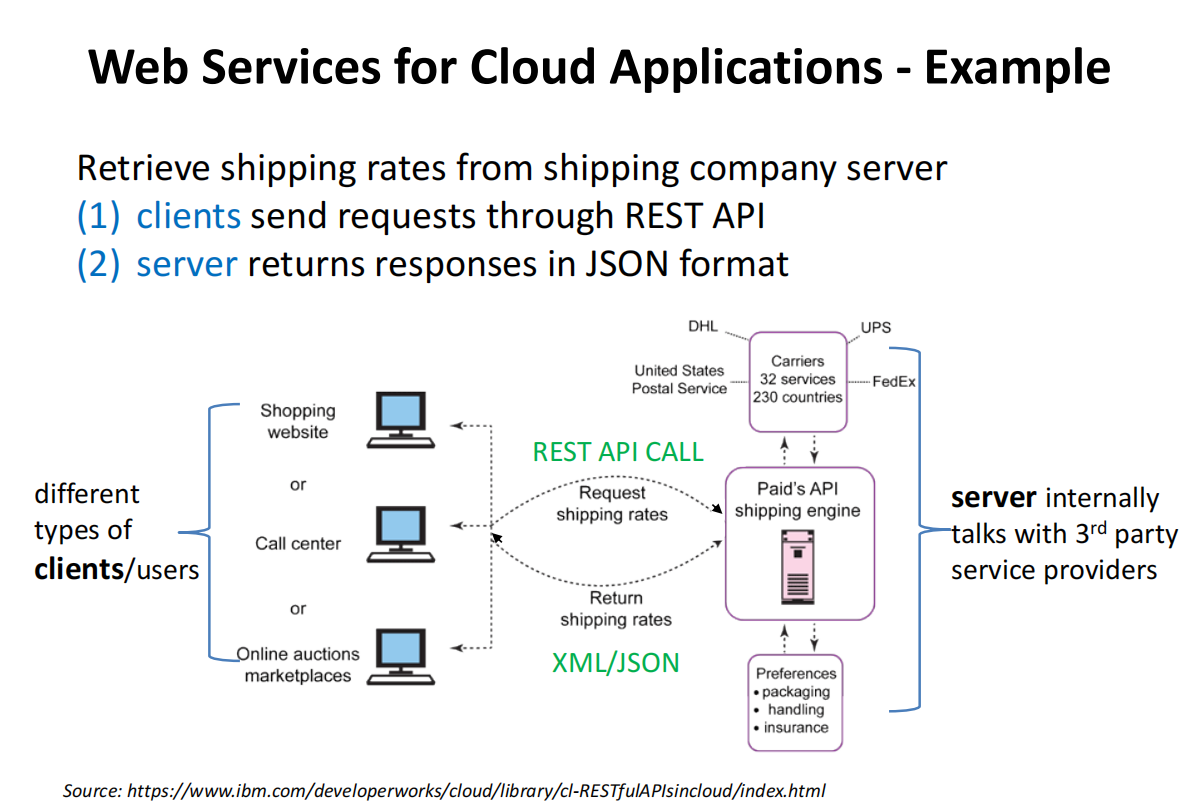
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) : Application protocol for web applications; defines a common web service messaging format for request and response message exchanges; based on the XML, uses TCP or UDP transport protocols.
Representational State Transfer (REST): software architecture for distributed hypermedia systems. Supports client communication with stateless servers, platform and language independent, supports data caching, and can be used in the presence of firewalls.
Rest is better in simplicity, flexibility, efficiency and scalability, which is suitable for web applications. SOAP is suitable for applications requiring higher security, transaction handling, and reliability, particularly in enterprise-level applications.
Cloud Application Development Models
Characteristics of Cloud Service Models
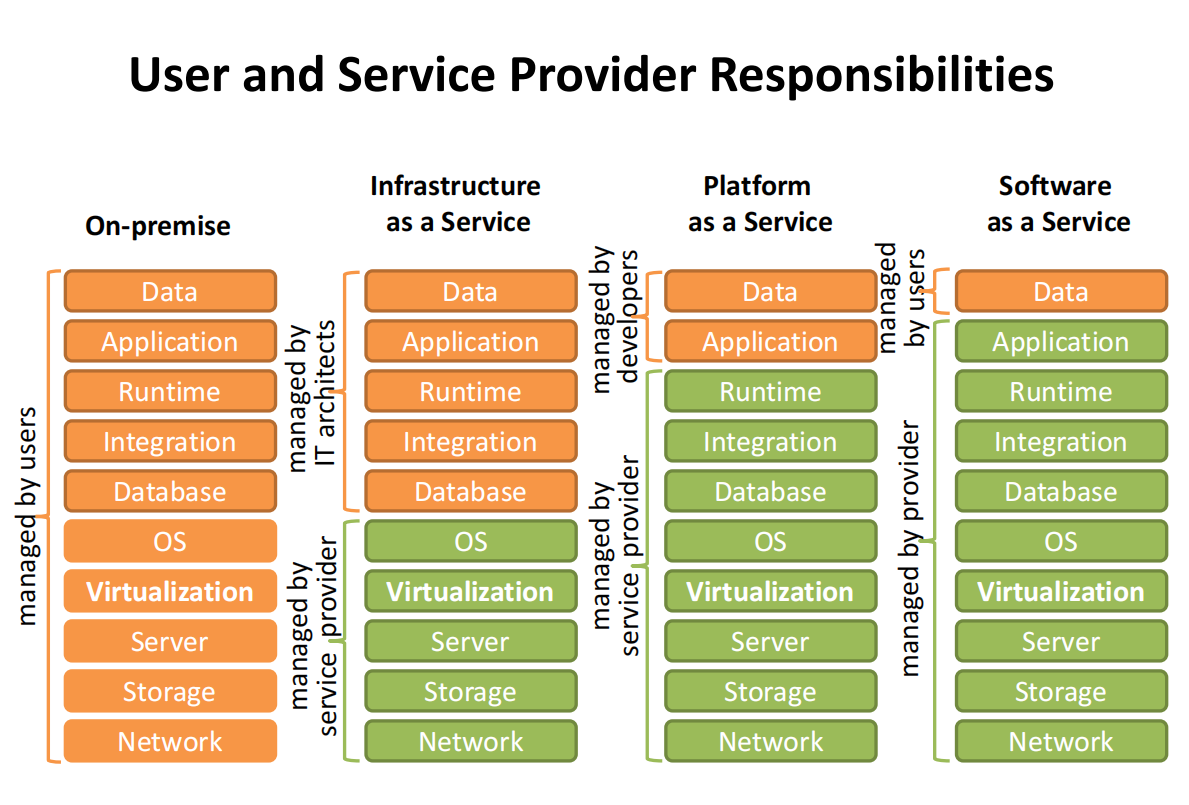
Infrastructure as a Service (for IT architects)
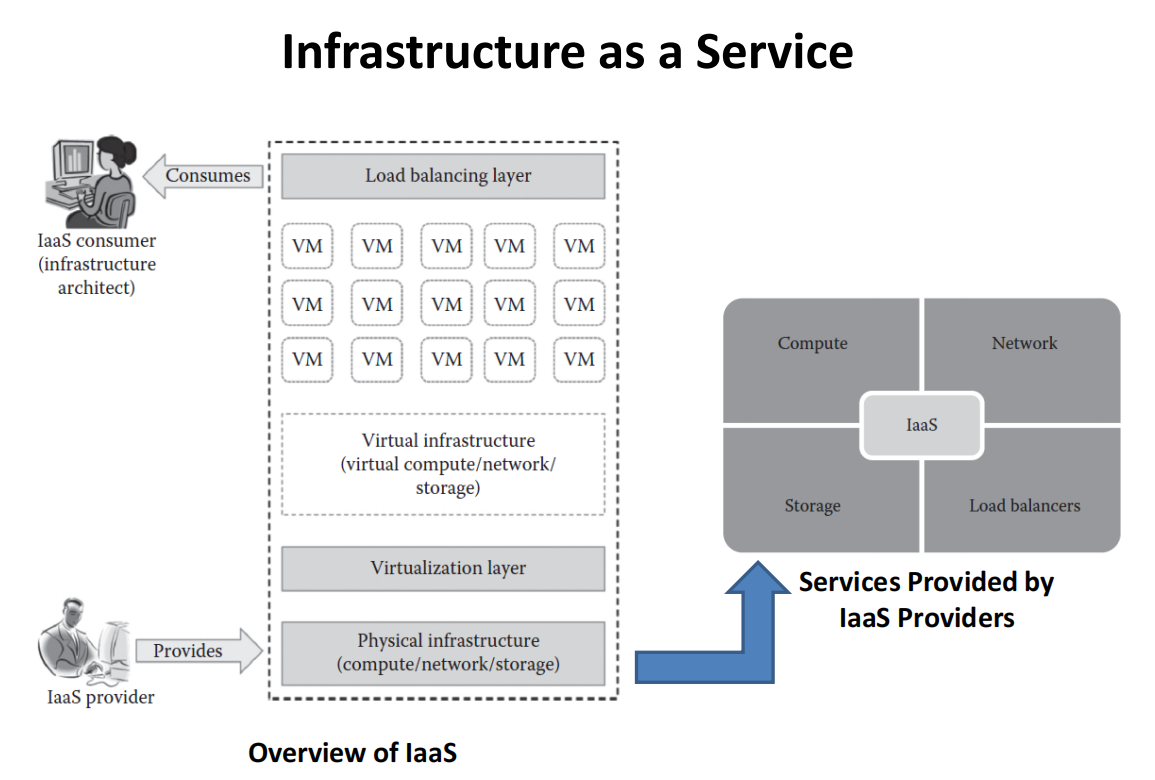
Web access to resources
Centralized physical resource management
Elastic services and dynamic scaling
Shared infrastructure across multiple users
Preconfigured VMs
Metered services
Platform as a Service (for developers)
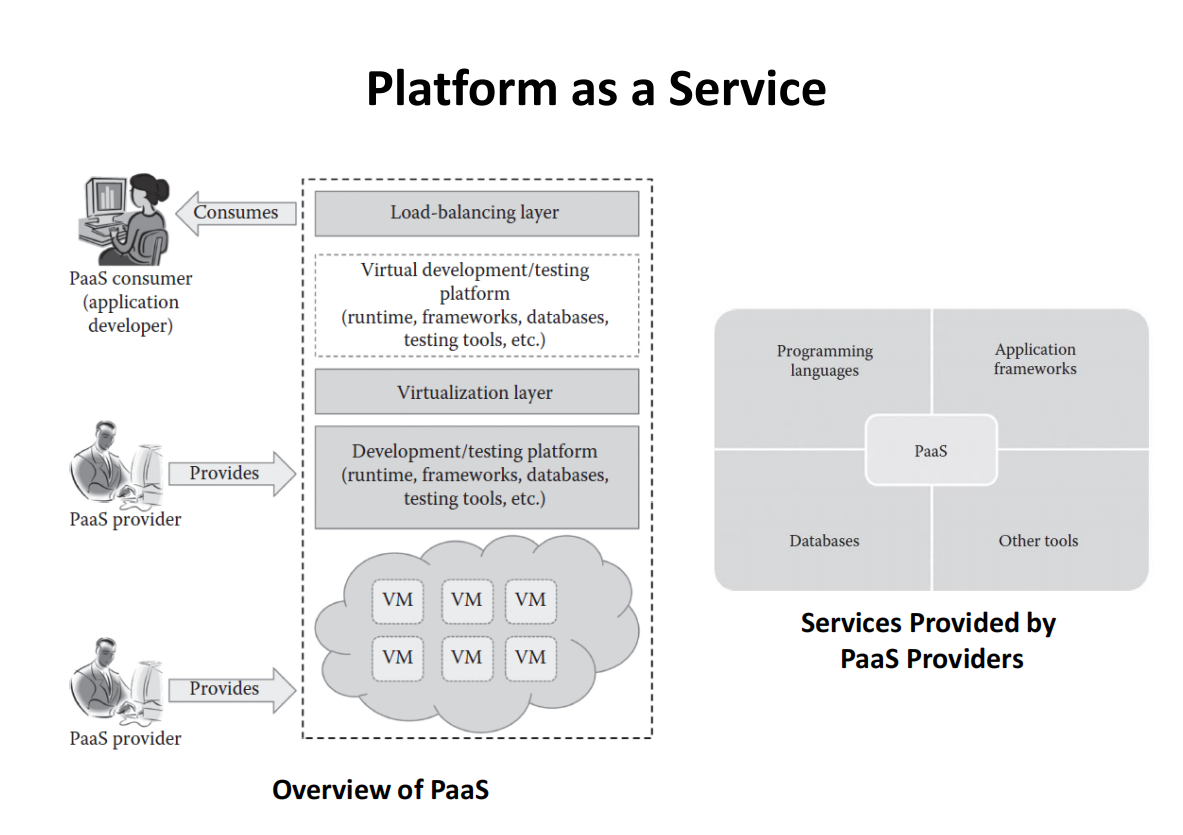
All in one – same IDE to develop, test, deploy, host and maintain applications
Web access to development platforms
Offline access for developers
Built-in scalability
Collaborative platform for developers
Diverse client tools
Software as a Service (for end users)
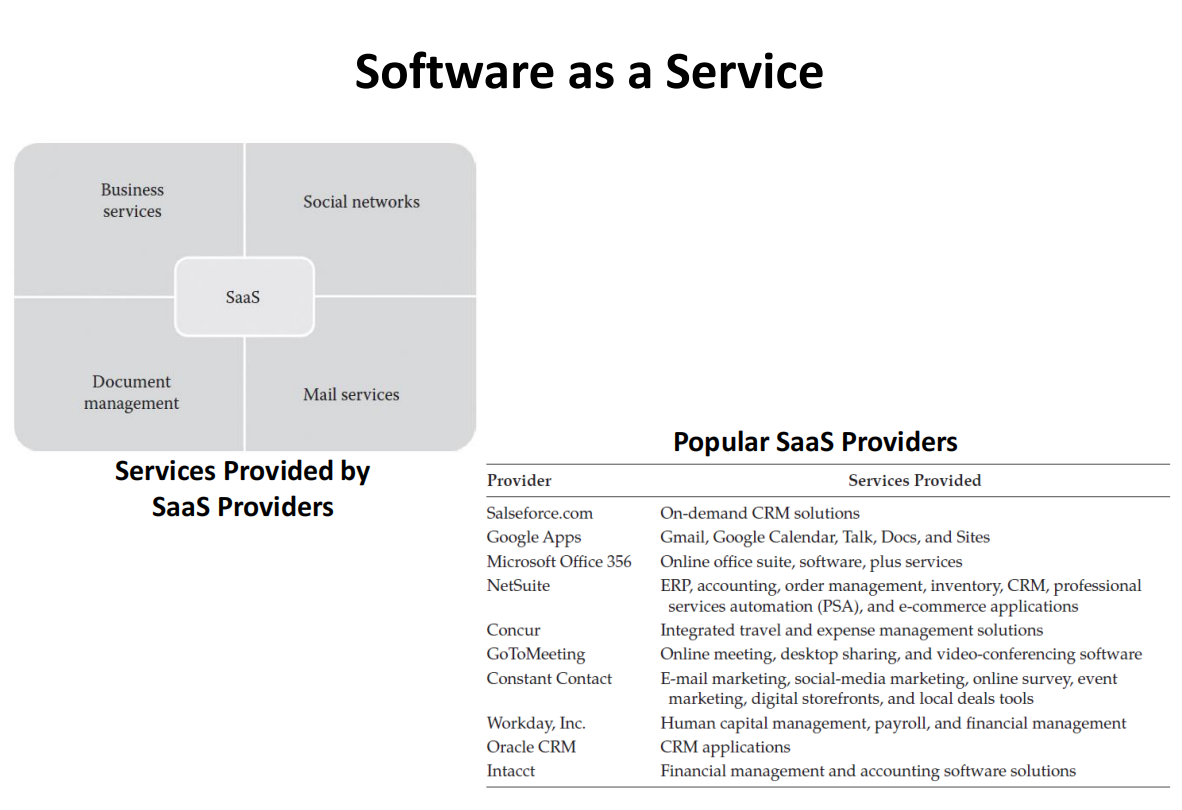
Multi-tenanted applications
Web access
Centralized management of SaaS services
Multi-device support
Scalability under varying loads
High availability
API integration with other software
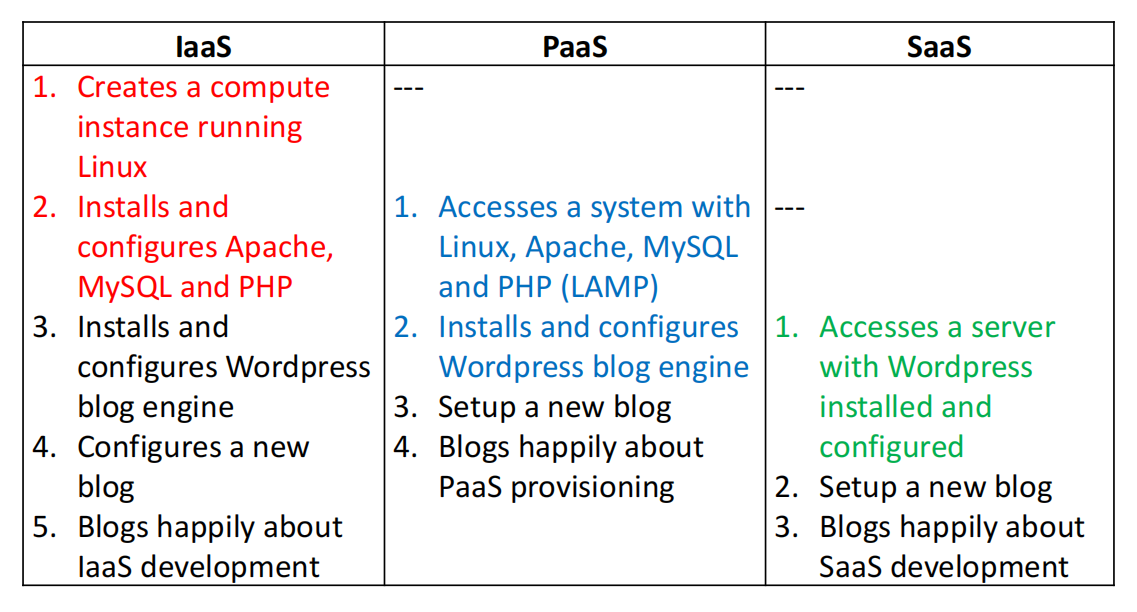
Examples of Setting up a Blog
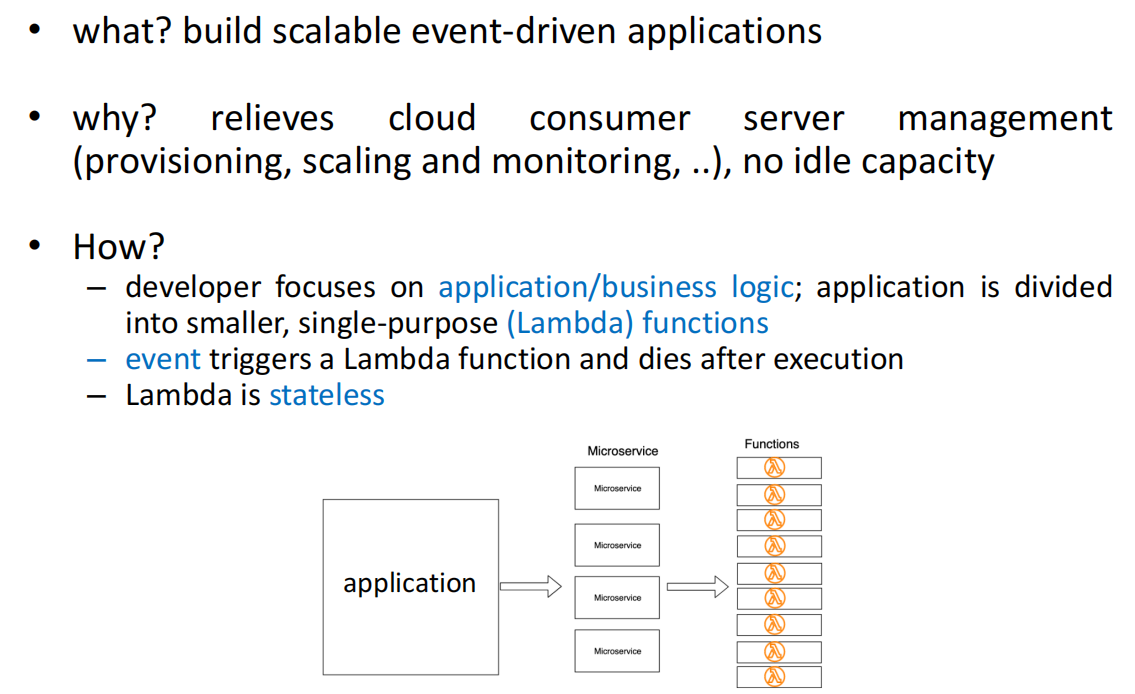
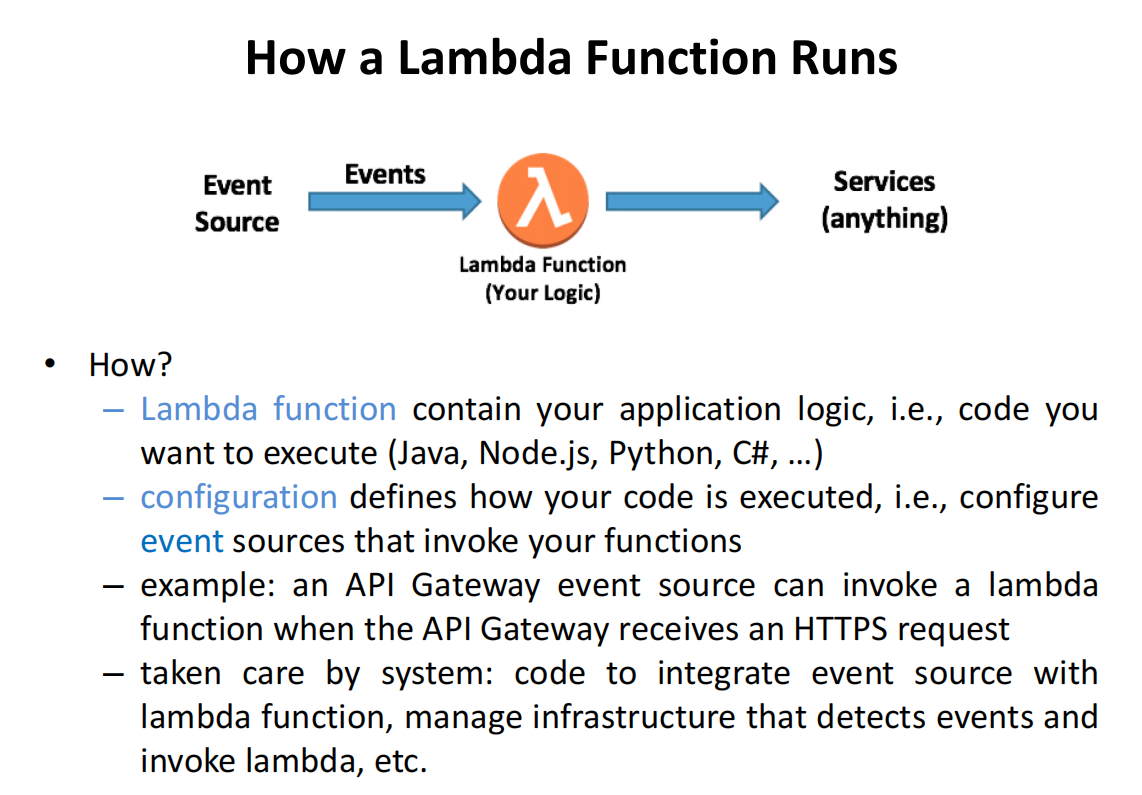
Bonus Track: Function as a Service