SWS3004-Lecture 1: Concepts and Models
L1 is about Concepts and Models of Cloud Computing.
Outline
- NIST Definition
- Cloud Characteristics
- Cloud Service(Delivery) Models
- Conceptual Reference Architecture
- Cloud Deployment Models
- Summary
Key Terms
Elasticity
On-demand self service
Pay-per-use (measured service)
Multi-tenancy (location independent resource pooling)
Cloud service (delivery) models
Cloud deployment models
Cloud actors
Definition
Cloud means "smooth" to access, control and measure. It has five essential characteristics, four deployment models and three service models.
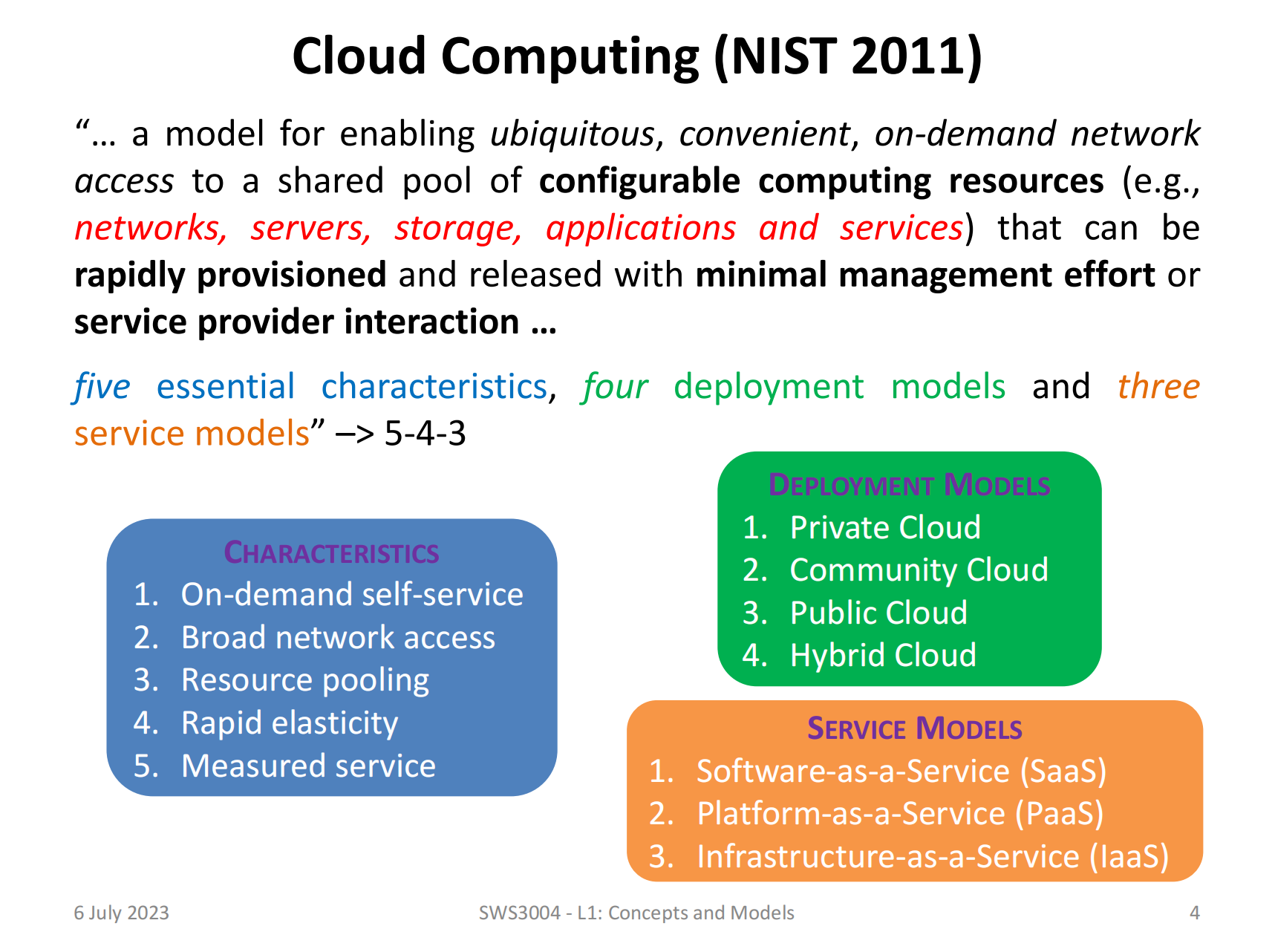
Cloud Characteristics
On-demand self-service through a service portal
With cloud computing, you can provision computing services, like server time and network storage, automatically. You won’t need to interact with the service provider. Cloud customers can access their cloud accounts through a web self-service portal to view their cloud services, monitor their usage, and provision and de-provision services.
Broad network access (ubiquitous access)
Users can access cloud services anytime and anywhere through a terminal device with network connection. Latency and bandwidth both count because they affect the quality of service.
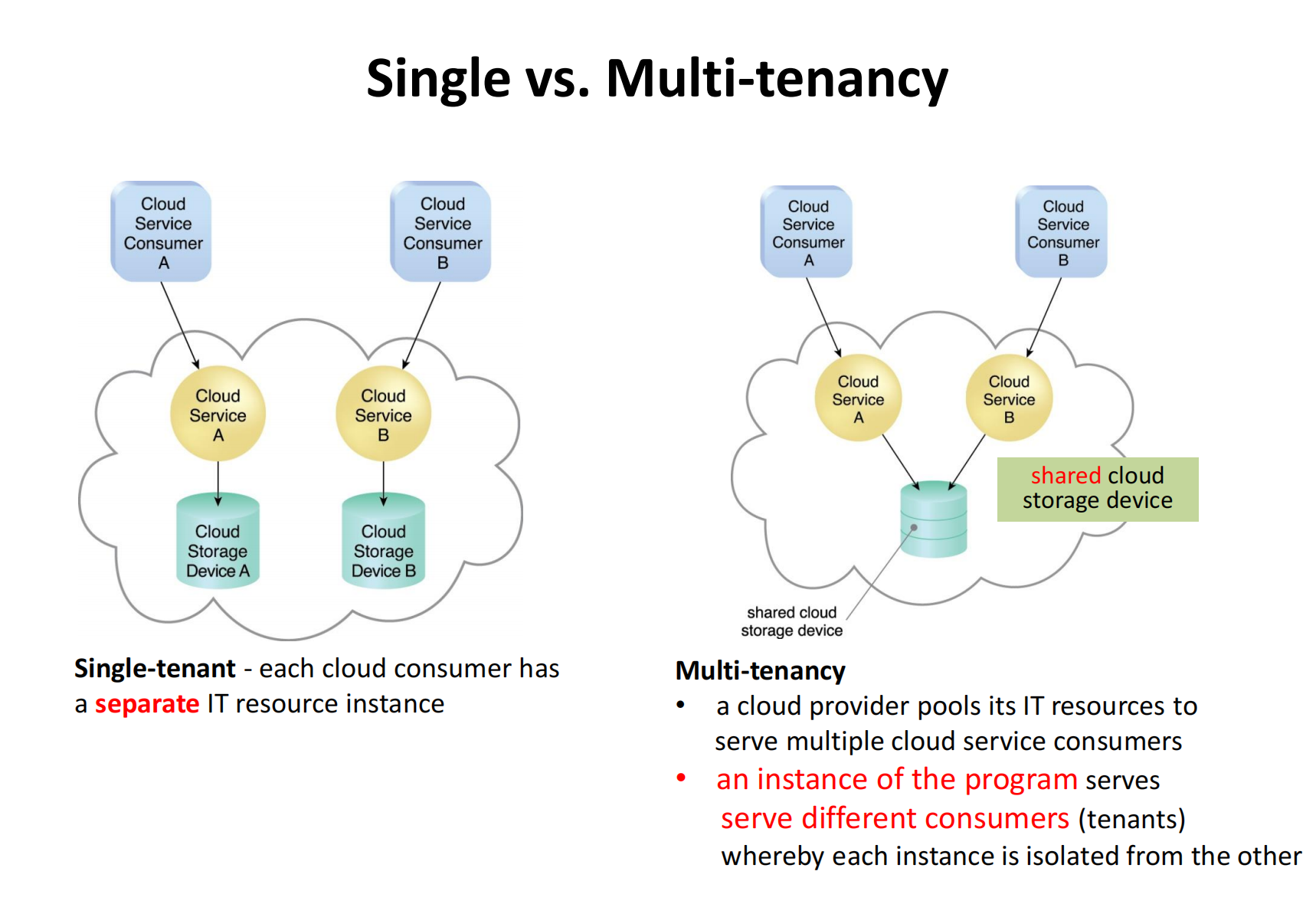
Location-independent resource pooling (multi-tenancy)
Computing resources are gathered together as pools, like CPU pools, memory pools, etc. With resource pooling, multiple customers can share physical resources using a multi-tenancy model. This model allows customers to share the same applications or infrastructure while maintaining privacy and security. It's a fantastic characteristic of cloud, which abstracts and subdivides physical resources.
Rapid elasticity – time to market / fast deployment
Cloud services can be elastically provisioned and released, sometimes automatically, so customers can scale quickly based on demand. With rapid and unlimited elasticity of cloud service, you don't need to buy hardware but use cloud resources to satisfy your demand.
Measured service (pay-per-use)
In cloud systems, a metering capability optimizes resource usage at a level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service. For example, you can use a measured service for storage, processing, bandwidth, and users. Payment is based on actual consumption by the customer via a pay-for-what-you-use model. Monitoring, controlling, and reporting resource use creates a transparent experience for both consumers and providers of the service.
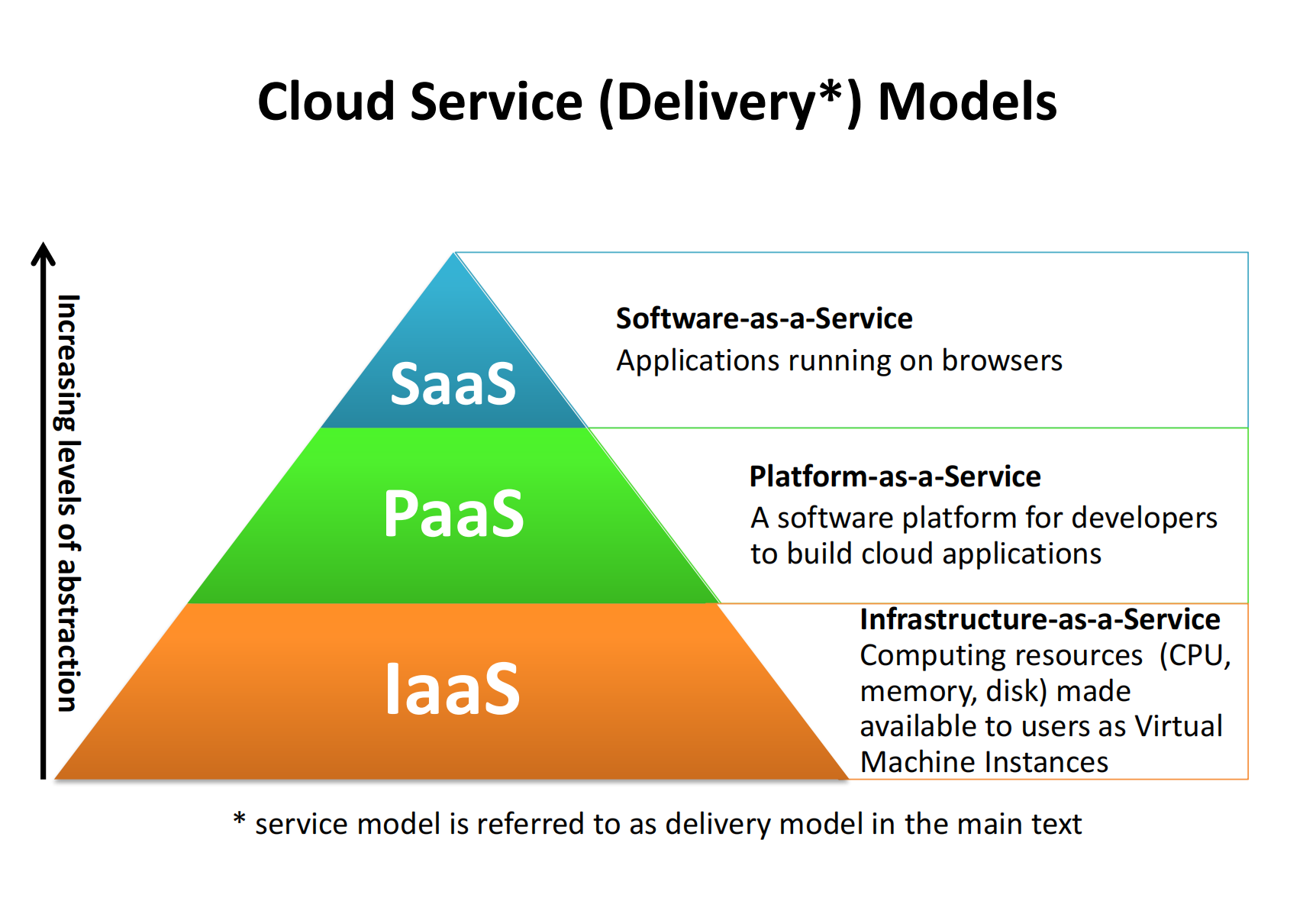
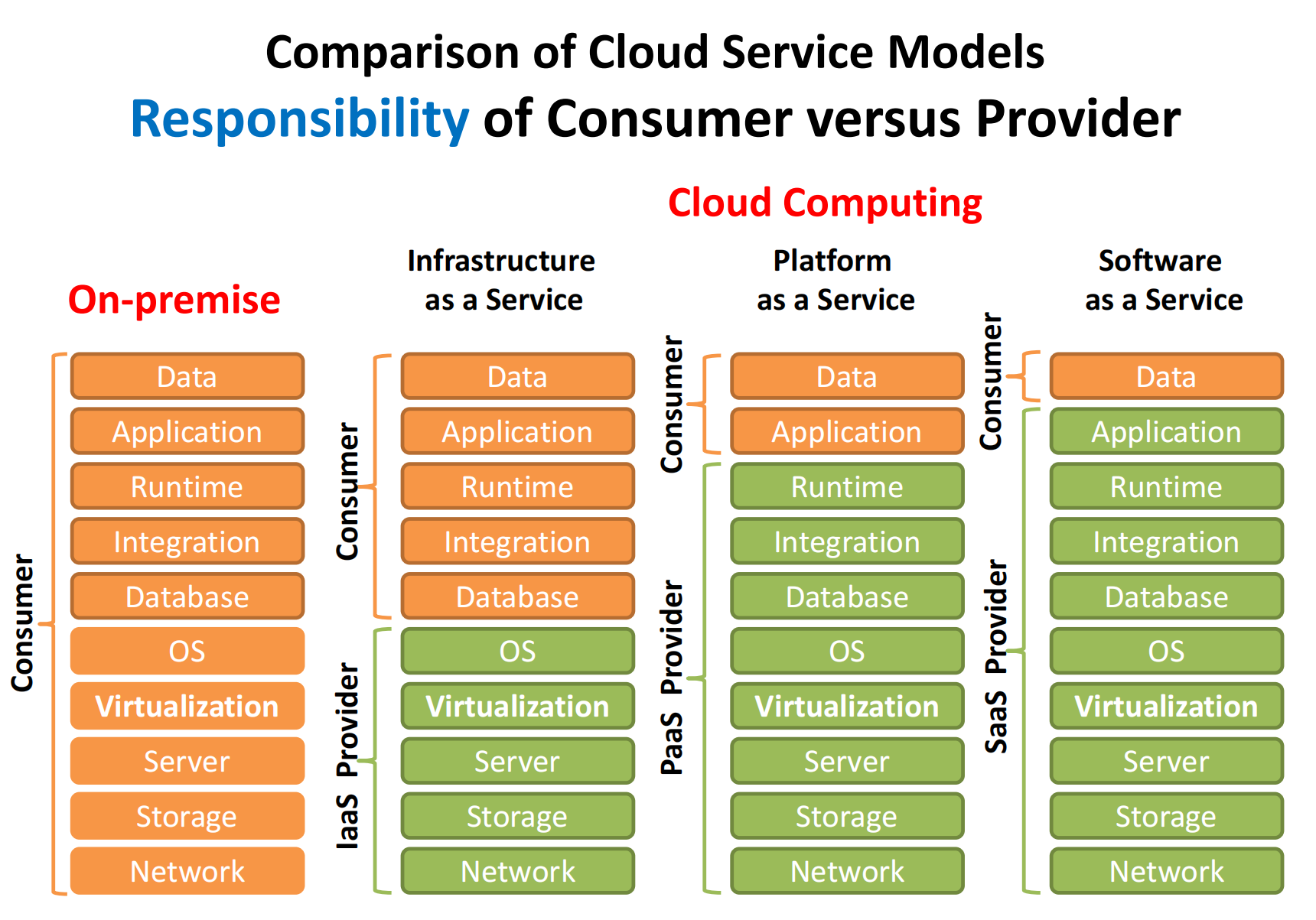
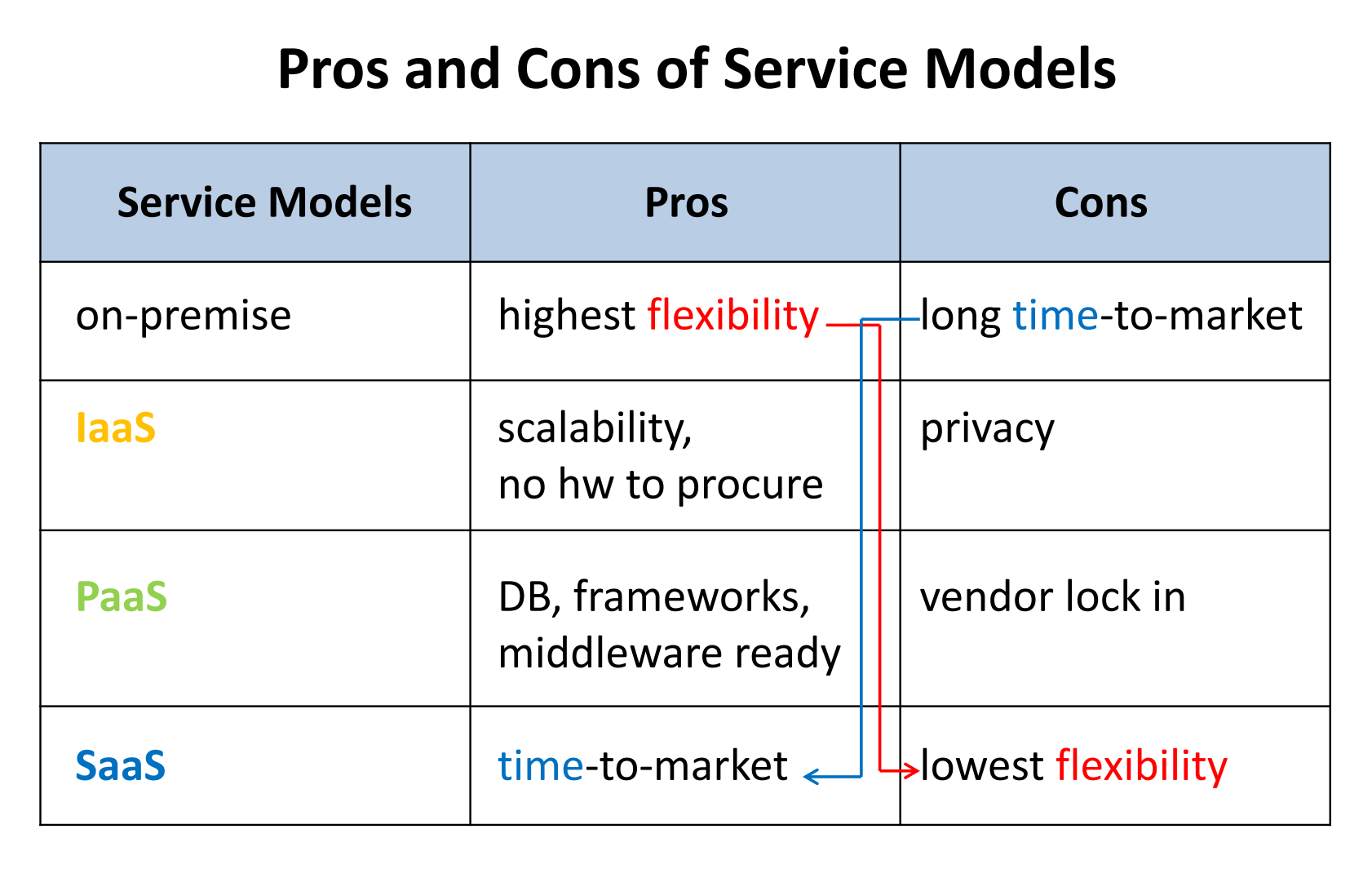
Cloud Service(Delivery) Models
There are three main models: SaaS, PaaS and IaaS. As for "steak" service, IaaS is like providing a kitchen with some pots, PaaS provides raw beef and pepper additionally, and SaaS provides a plate of steak. More convenience, but less space to select.
Conceptual Reference Architecture
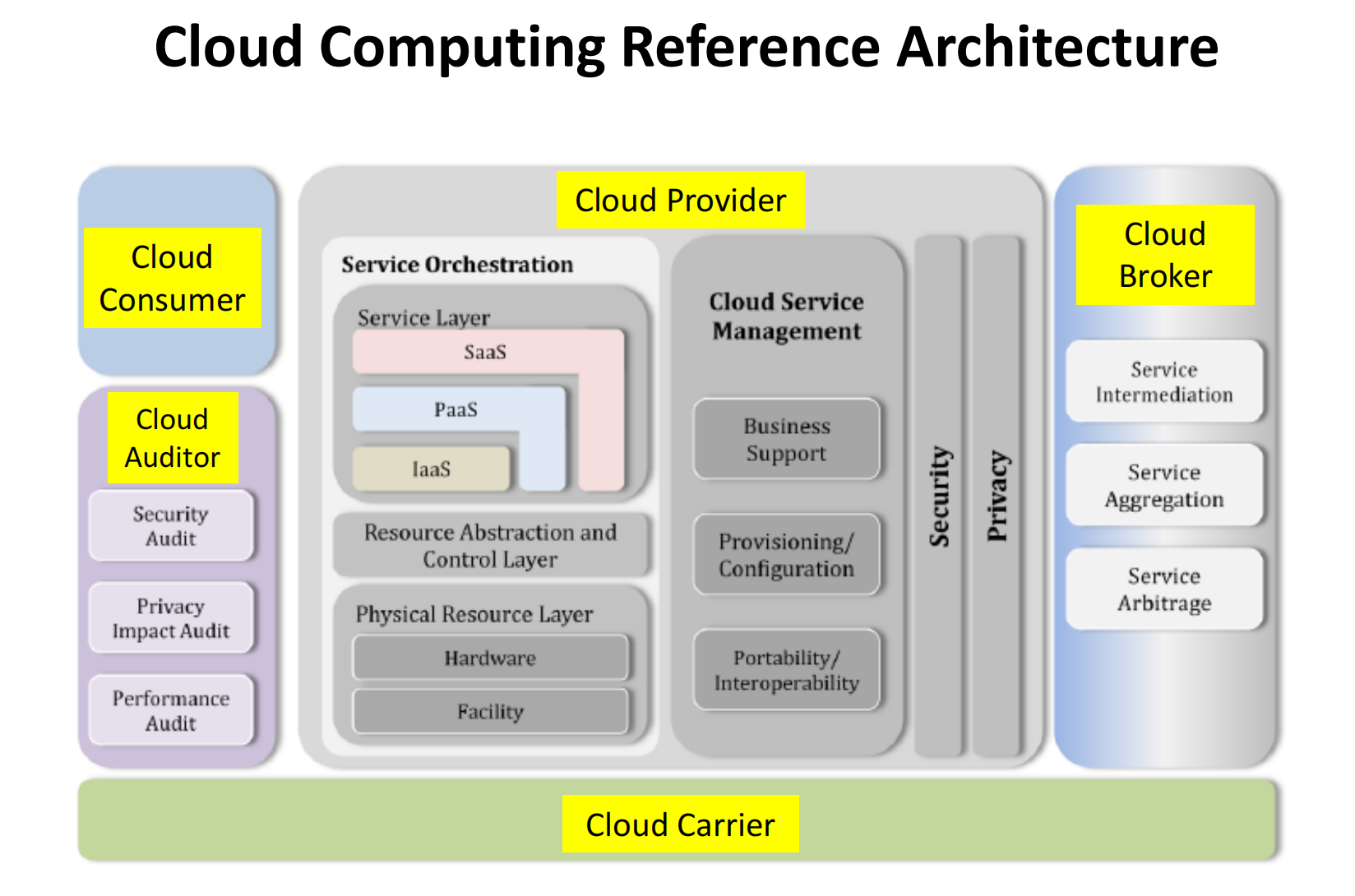
Actor Roles
Cloud Consumer - maintains a business relationship with, and uses service from Cloud Providers.
Cloud Provider – offers a cloud service to cloud consumers.
Cloud Auditor - conducts independent assessment of cloud services, system operations, performance and security of the cloud implementation.
Cloud Broker - manages the use, performance and delivery of cloud services, and negotiates relationships between Cloud Providers and Cloud Consumers.
Cloud Carrier - provides connectivity and transport of cloud services from Cloud Providers to Cloud Consumers.
CLOUD DEPLOYMENT MODELS
- Private cloud
- solely for used by an organization
- for enterprises/corporations with large scale IT
- Public cloud
- available to general public, i.e., shared by all consumers
- open market for on demand computing and IT resources
- concerns: limited SLA, reliability, availability, security, trust
- Community cloud
- shared by several organizations and supporting a specific community
- Hybrid (federated) cloud
- two or more public and private clouds that interoperate
- extends private cloud(s) to include a shared public cloud